CCPROG1_process_and_importance
The Process and Importance of Programming
Quote
Computer Programming is an art, because it applies accumulated knowledge to the world, because it requires skill and ingenuity, and especially because it produces objects of beauty -Donald Knuth
Some Terms
- Programming - process of writing a program
- Program - series of instructions that makes a computer perform a particular operation
- Programmers - people who write programs
- IDE - Integrated Development Environment
- DLC - DownLoadable Content, a launch or patch that improves quality and processes
- Programming Language - set of rules, words, etc. used for writing computer programs
- ex. Java, Python, Visual Basic, Ruby, C
- Coding - converting algorithms/Flowcharts into an actual programming language
- Pseudocode - Algorithm written in natural language with a programming language-like format, normally written for ease of understanding
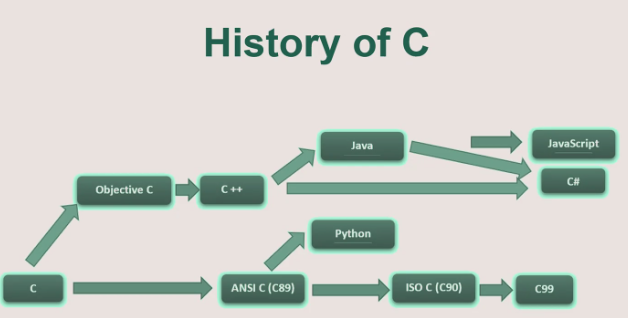
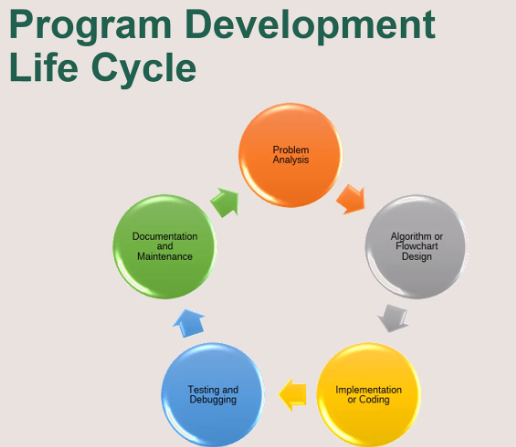
History of C and The Program Development Life Cycle
Problem Analysis
- Identify and understand the problem
- Identify the input and output of the program
- Gather all relevant information to solve the problem, and consider if there are any constraints or conditions present
Setting up Algorithms to Solve Problems
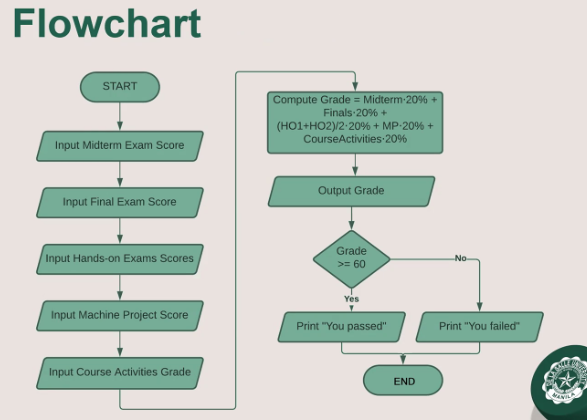
An algorithm is a list or sequence of steps that will solve the given problem. They are in natural language, such as English or Filipino
Example:
- Ask the user to input the midterm exam score.
- Ask the user to input the final exam score.
- Ask the user to input 2 hands-on exam scores HO1 and HO2
- Ask the user to input the machine project score.
- Ask the user to input the course activities grade.
- Computer the grade using the formula $$ grade = Midterm \cdot 20% + Finals \cdot \frac{HO1+HO2}{2} \cdot 20% + MP \cdot 20% + CourseActivities $$
- Display/Output the grade.
- If the great is greater than or equal to 60.0, display "You passed!", otherwise, print "You failed!"
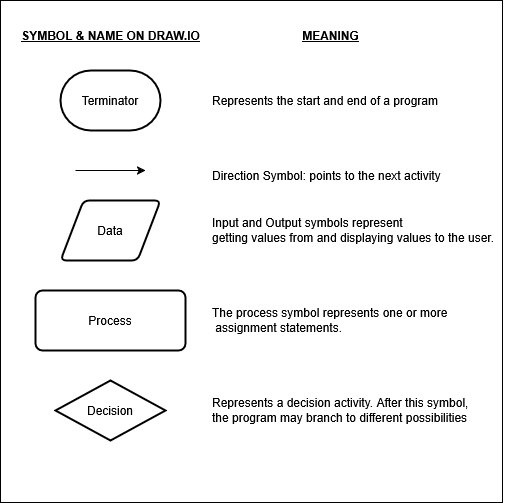
Flowcharts
Flowcharts are a graphical representation of a list or sequence of steps to solve the given problem.
Testing, Debugging, Errors
- Bugs - errors in the program
- Debugging - process of removing/correcting the errors
- Test Cases - set of actions performed on a program/system that's made to find bugs in the program. Makes sure that it's working as expected. (Geeks4Geeks: Test Cases)
Types of Errors
- Syntactical errors - caused by deviating from grammatical rules of the language
- Logical errors - caused due to faulty algorithm formulation
- Compile errors - occurs when syntax errors are encountered while translating the program code into a form that the physical computing machine can understand; code works but gives wrong output.
- Run-time errors - an effect of logical errors, appear during the execution of the program; causes the program to crash (ex. infinite-loop)
Documentation
Written text that is embedded into a code or written separately, it explains the source code or how the software operates, and/or how to use it.
Types of Documentation
- User's Manual - a step-by-step instruction on how to use the program
- Internal Documentation - comments included in the program regarding how the program was designed and created
- Technical Manual - printed details on how the program was designed and created.
Why should you do documentation?
- For ease of understanding different parts of the code.
- Reduces efforts during program maintenance and problem reconstruction.