STCLOUD_async5b cloudcomp recap adv of cloud intro to amazon web services
This note is ready but there needs to be a redo of the images
Agenda
- Recap of Definition of Cloud Computing, Infrastructure as HW/SW, Cloud Service Model, and Cloud Deployment Models
- Discussion of the Advantages of Cloud Computing as well as Web and Cloud Services
Recap of Section 1: Introduction to cloud computing (AWS)
Cloud Computing (re)defined
We redefined cc as: Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of computing/IT resources via the network.
- where Cloud refers to public AND private cloud. (AWS is a public cloud)
- where network is via the internet or intranet (Geeks4Geeks: Internet vs Intranet) - double check this, but the idea is that it's either on the internet or local
Infrastructure as Software
Cloud computing, because of virtualization, enables you to stop thinking of your infrastructure as hardware, and instead think of (and use) it as software.
- cloud computing is a methodology while virtualization is the technology
- gives you benefits of flexibility, agility, and speed
Traditional Computing Model
- infrastructure as hardware
- hardware solutions:
- require space, staff, physical security, planning, and capital expenditure (CapEx, upfront payments)
- plan, for example, a 6-month duration. you have to guess how much resources we need by guessing.
- have a long hardware procurement cycle (it takes long to get them, you have to wait)
- procurement cycle: bidding, suppliers, equipment, delivery, setup, etc.
- require you to provision capacity by guessing theoretical maximum peaks
- when the equipment arrives, how much resources do we actually need?
- require space, staff, physical security, planning, and capital expenditure (CapEx, upfront payments)
because we have a theoretical max peak → delay → overestimation or underestimation
- overestimation or underestimation causes losses in one way or another
- overestimation: when you thought you needed 2 servers but you needed 1 server lang pala, you can't maximize it and it's a huge waste of money
- underestimation: when you thought you needed 2 servers but you actually need 3 servers
Cloud Computing Model
- infrastructure as software due to virtualization
- software solutions:
- are flexible
- can be reconfigured: can change more quickly, easily (self service and ease of use), and cost-effectively than hardware solutions
- eliminate the undifferentiated heavy-lifting tasks (racking and stacking servers, setting them up, etc.)
- the cloud service provider take care of that
Cloud Service Models (options)
- we have varying levels of virtualization so that we have options.
- those options vary on the level of flexibility and control that you want → those are defined as the cloud service models
- these models are defined also in how much knowledge the user has regarding the setup and configuration that they want
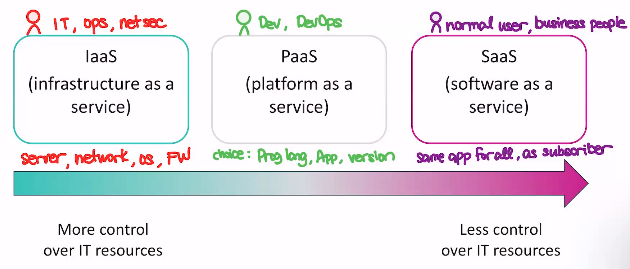
- IaaS (infrastructure as a service, more control over IT resources)
- focuses on the low level resources, giving you the highest control over the IT resources
- server, network, OS, firewall
- chosen by individuals in the IT field, operations, network security
- PaaS (platform as a service, some control but above the OS so apps and above)
- programming language, app, version
- chosen by individuals in development and devops
- SaaS (software as a service, less control over IT resources)
- same application for all, when you use it you're a subscriber or user
- chosen by individuals who are just normal users, or business people
- Example: Google Suite, Microsoft 365
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Organizations that may need a global reach might go for cloud, those that don't may go for on-premises or private cloud. It depends on the use case. You're given the choice.
- Cloud
- lower CapEx, higher OpEx (due to outsourcing)
- public cloud via internet
- Public cloud usually has global scale and reach
- Rent resources (focused on rental aspect)
- Examples: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
- Hybrid, best of both
- Public + Private cloud (you save more money)
- Private can use minimum resources
- Public cloud to rent when usage changes (more resources needed) ("Scale up" using private cloud)
- On-premises/Private-cloud
- higher CapEx, lower OpEx
- private cloud
- can be via the network or accessed via the internet, you can completely remove access to the internet and it will still work if you're on-premises
- has more security, and you have full control & responsibility
- Examples: CCSCloud, ALTDSICloud
Recap ends here
Continuation of Section 1: Introduction to cloud computing (AWS)
Similarities between AWS and Traditional IT
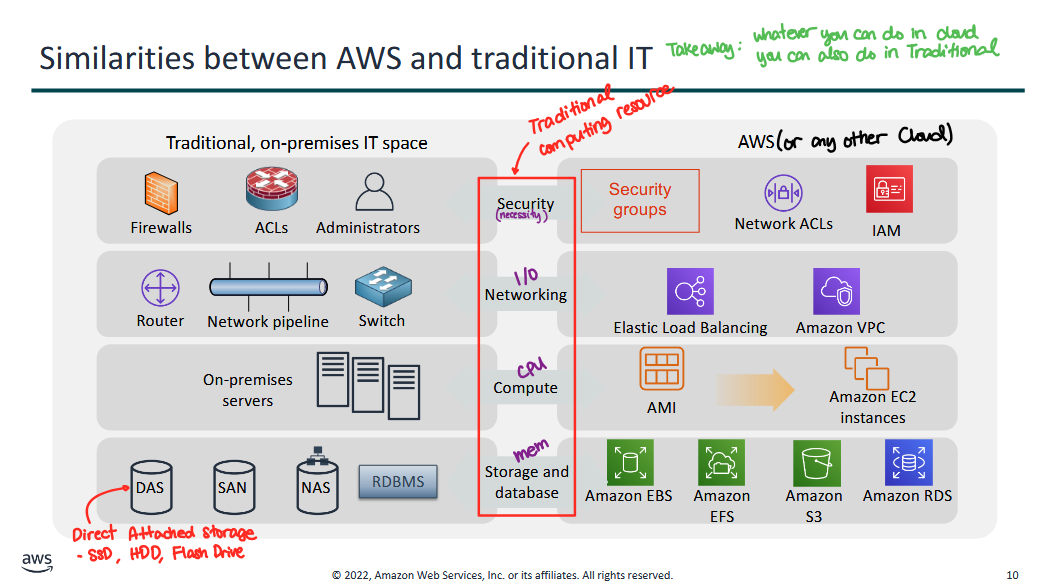
- Whatever you do in cloud, you can also do in traditional (and a bit more), and vice-versa → don't be afraid of change!
- Main point: we have solutions in traditional that are also available in cloud
Four Categories (representative of Traditional Computing Resources)
- Security (is a necessity)
- Traditional: Firewalls (huge if statements with a lot of conditions to allow or deny traffic), ACLs (network firewalls, conditional statements on the network devices to allow or deny traffic), Administrator (Ex. Active directory for managing user accounts)
- Cloud: Security Groups (host-based firewall), Network ACLs, IAM (directory management system by AWS)
- Network (I/O of data, and how we interact with web services)
- Traditional: Router, Network pipeline, Switches
- Cloud: Elastic Load Balancing (network load or traffic balancing), Amazon VPC (virtual private cloud, your own private network in the cloud; VPC is like switches and routers)
- Compute (CPU)
- Traditional: on-premises servers
- Cloud: AMI → Amazon EC2 instances
- Storage and Database (Memory)
- Traditional: DAS (Direct Attached Storage like SSD, HDD, flash drives), SAN, NAS, RBDMS
- Cloud: Amazon EBS (block storage), Amazon EFS (file system, network based storage), Amazon S3 (object storage), Amazon RDS (relational databases)
Section 2: Advantages of Cloud Computing (AWS)
1. Trade Capital Expense for Variable Expense
focused on the idea of options in terms of accessibility (note: CapEx is not always bad, it could help you save some money in the long run)
-
capital expenses are CapEx, upfront payments → ok for large companies
-
variable expenses are OpEx, recurring payments → ok for startup or testers
-
Traditional: Data center investment based on forecast by buying servers
-
Cloud: Pay only for the amount you consume by renting servers
2. Massive economies of scale
bulk use and purchase leads to discounts and savings, because of aggregate usage (massive usage) from all customers, cloud can achieve higher economies of scale and pass savings on to customers.
- customers usually buy things in bulk (like servers and services in bulk)
- the main idea is, because of the massive amounts of stuff that customers (startups, testers, business people, etc.) buy, the cloud service provider can give back to them in discounts
Example:
Service provider A buys 1 server for 1m x 100 = 100m in costs → 10k/month
Service provider B buys 10 servers for 9m x 10 = 90m → 9k/month
- that's a better deal for the same server
- better deal → happy customer → they rent more → cloud provider gets more money so they can buy more → cloud services become cheaper because of bulk use and purchases
3. Stop guessing capacity
in traditional, you have to guess and there's a long hardware procurement cycle → with cloud, you don't need to guess if you rent
- long procurement cycle: there's a delay between wanting and having the resources
- Traditional: overestimated server capacity → waste of money
- Traditional: underestimated server capacity → service becomes slow
- Cloud: scaling on-demand → you can rent more/less depending on your needs and it's instant
- you're paying for a premium but you're able to catch the market trend → you earn more, and can afford the increased cost
4. Increase speed and agility
cloud uses virtualization. with virtualization, you treat your infrastructure as a software.
- hardware solutions take time: weeks to months between wanting and having resources
- software solutions are flexible and agile: minutes between wanting resources and having resources, you can easily deploy and configure
5. Stop spending money on running and maintaining data centers
this is more about where you put your money, rather than savings.
- Traditional: you have to micromanage your money when you're running your own data centers
- When you invest in cloud: you outsource management for a premium but earn more money by focusing on your business and customers
6. Go global in minutes
cloud service providers have regions and datacenters all over the world, so if you deploy your (cloud) servers closest to the location of your users you reduce latency → and that improves user experience
- there's higher latency if your users have to go far by having your server far from your users.
- if your users are in the Philippines, but you're in the Philippines also, maybe going global won't be an advantage and will be a waste of money.
Section 3: Introduction to Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- introduction to AWS and cloud services
What are web services?
The cloud works by having its services integrated together via standard formats and APIs. These services are developed to be integrated together.
- a web service is any piece of software that makes itself available over the internet or network and uses a standardized format - such as Extensible Markup Language (XML) or JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) - for the request and the response of an application programming interface (API) interaction.
- standardized formats makes things accessible and easy to understand regardless if you're using a different format (you can just use a translation)
- APIs let us make software applications that can interact with other things
Categories of AWS Services and other cloud provides
there are many services and options to choose from depending on your need and use case.
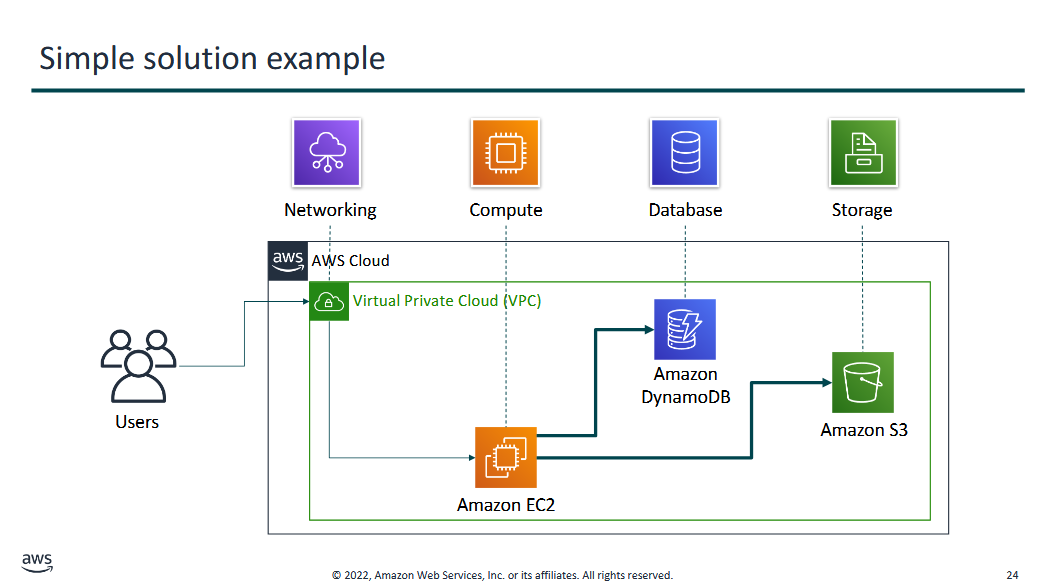
Sample solution example:
Cloud has APIs that lets us connect services together.
- Amazon EC2: VM
- Amazon DynamoDB: database
- Amazon S3: storage
- the solution could be a website that's hosted on the cloud
Choosing a Service
the point is: there are many services/options to support needs of different users and use cases
- the service you select depends on your business goals and technology requirements
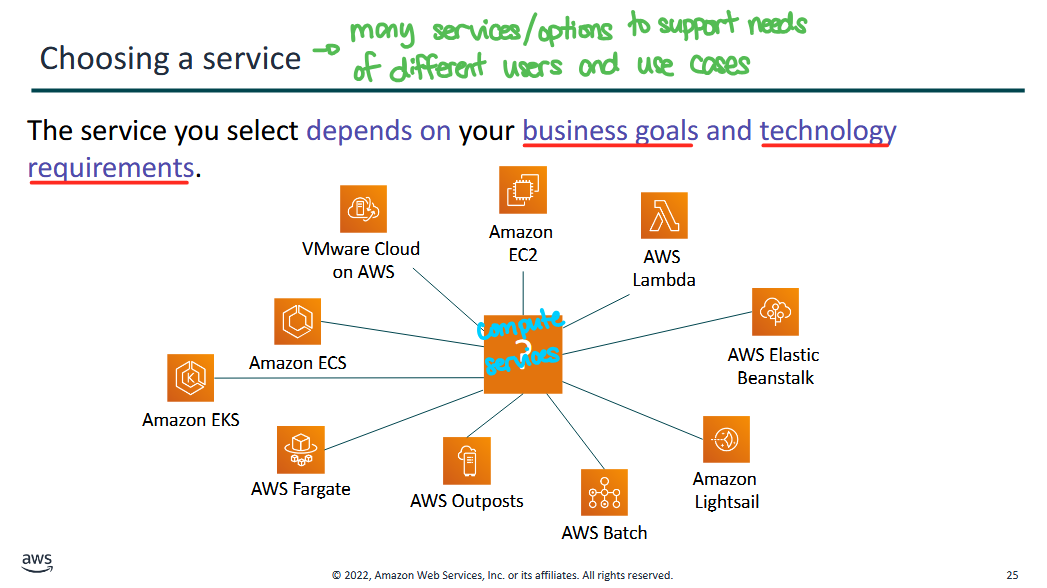
- Amazon EC2: virtual machines
- AWS Lambda: serverless
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Amazon Lightsail: web orchestration, web
- AWS Outpost: have cloud but go hybrid and have your own datacenter
- AWS Fargate, ECS, and EKS: container management
Ways to interact with AWS and other cloud providers
- AWS Management Console: an easy-to-use graphical or web interface
- used by students, testers, business people
- Command Line Interface (AWS CLI): access to services by discrete commands or scripts
- good for automation and batching
- used by IT, Ops, Network Security
- Software Development Kits (SDKs): access services directly from your code (such as Java, Python, and others)
- code → means you can make custom applications
- used by devs and devops
Cloud Adoption Framework: Six Perspectives
things to think about before you go cloud or not
From a business perspective... (business capabilities: Will your business benefit?)
- business: is it beneficial to your business? do you need a global scale?
- people: do you need to train them? are they familiar with cloud?
- governance: how do you manage your users, your setup, etc.? policies, procedures, certifications?
From a technical perspective... (technical capabilities: Are you ready technologically?)
- platform: are there platforms/services that you can use for your setup? can you put your data center there and it will be enough? are the solutions ready for you to use?
- security: are you able to setup the same level or even better security (from the traditional setup) by going to the cloud?
- operations: what are the day-to-day operations? is it ok for WFH setup?