STCLOUD_intro to virtualization and cloud - trad vs virt vs cloud
RAW FILE
This note has not been edited yet.
Traditional Computing vs Virtualization Computing vs Cloud Computing
```col-md
flexGrow=1
===
# Traditional
- on premise w/ the user, local only, physical hardware
- one OS at a time, or you can dual boot, change OS, get a new PC ahahahha → compatibility issues
- dedicated machine/PC
- dedicated servers (web servers, DB, email servers) to be able to scale up → one machine is fully for web servers, etc.
- based on the application you're using at the current time
- there would be issues in resource maximization because you're not running all the services + people won't be accessing your website server when they're asleep
- advantages: local only, not too much latency + on premise with the user (on prem), can fix physical hardware
```
```col-md
flexGrow=1
===
# Virtualization
- virtual machines, containers/dockers
- dockers are running containers
- containers are OS virtualization (WSL Windows Subsystem for Linux - borrows OS functionality and subsystem files from the host machine)
- hardware virtualization as if it has a "physical computer"
- vbox, vmware, parallels, emulation, simulation, mimic
- virtual representations of physical things: VM, virtual desktop, VPN, vNetworks
- VPN creates an encrypted point-to-point connection
- different environment (multi-OS)
- cloud: methodology/usage of virtualization
- Scenario A: your computer SSH AnyDesk Server then the tech guy uses an AnyDesk client
- Scenario B: you're both connected to the cloud, accessing a VM away from urself. you can make it 16GB and get the resources from the cloud but there will be latency issues
- resource sharing (between the Host Machine and Guest Machine)
- Host Machine: Physical
- Guest Machine: Virtual, shares with the host
- customize → you can copy, easily transfer, etc. because it's just software → ENCAPSULATION
```
```col-md
flexGrow=1
===
# Cloud
- was creative as a self service (allowing you to subscribe and setup your resources by yourself)
- expensive* (buying servers is more expensive)
- renting resources (it's a rental service)
- subscription, pay as you go/use (you won't get it anymore if you stop paying for it)
- powerful → servers in datacenters & AZ & regions(geographic, locations far from each other)
- practical on a global scale, has global reach
- user friendly, automation
- service models: SaaS, Paas, Iaas
- SaaS -> gdrive, gdocs
- PaaS → cpanel (with version, language)
- reliability, redundancy, etc. if you select a certain region
```
Summary
- Traditional: physical hardware
- Virtualization: mimics physical hardware, different environment (multi OS)
- Cloud:
Traditional Computing
-
refers to the use of physical servers and datacenters to deliver computing and other IT services
- each server is a dedicated setup
-
used to be the practice during the early days of using computers in companies and organizations, where dedicated servers are the commonly used
-
the host computer would be installed with a single OS directly on the hardware, where tools, dependencies, and applications would run from it
-
would typically run one or a few applications per machine, resulting in possible issues in resource allocation as well as difficulty in scaling
-
predictable and easy scale-up
-
if you want a Windows Server 2008 and another OS Windows Server 2012, you'll need two versions of servers and separate computers.
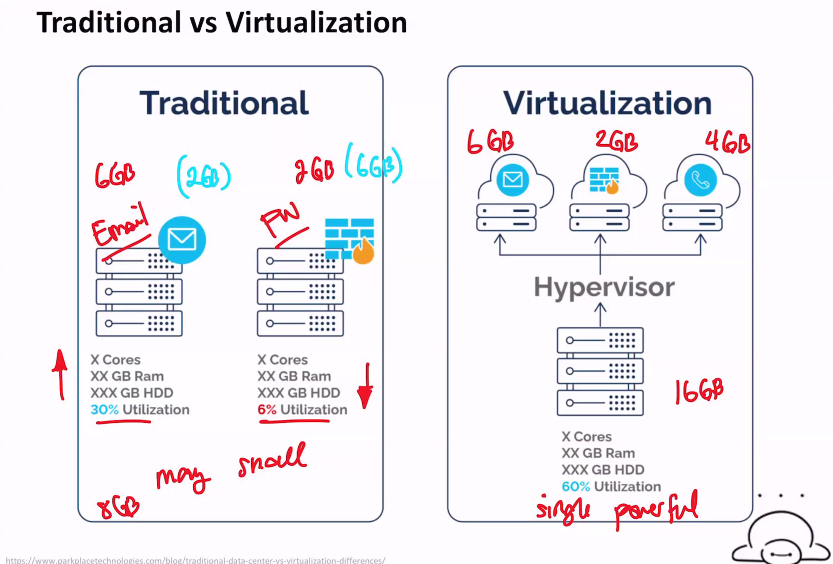
- instead of many small computers, you'll have a single powerful computer
- virtualization has better resource utilization
Virtualization
- technology that you can use to create virtual representations of servers, storage, and networks and other physical machines and resources
- mimics the functions of physical hardware to run multiple virtual machines simultaneously on a single physical machine
- a virtual computer system is known as a virtual machine or VM is a self-contained (all data and files are complete within itself), completely independent (exist by themselves, not dependent on the host), and isolated software container with an operating system and application inside
- multiple VMs on a single computer results in several OS and applications to run on one physical server, or host
- if you get malware, it will be isolated from the host computer
- a virtual machine is a FULL computer, it's just digital
Without Virtualization
- due to the limitations of x86 servers, many IT organizations must deploy multiple servers, each operating at a fraction of their capacity (wasteful), to keep pace with today's high storage and processing demands
- the result is huge inefficiencies and excessive operating costs
With Virtualization
- virtualization relies on software to simulate hardware functionality and create a virtual computer system
- enables IT organizations to run more than one virtual system (multiple OS and applications on a single server → better compatibility)
- result is economies of scale (instead of buying many small computers) and greater efficiency (manage resources more efficiently)
Deployment using Traditional vs Virtualization
- 3 servers on the left (traditional)
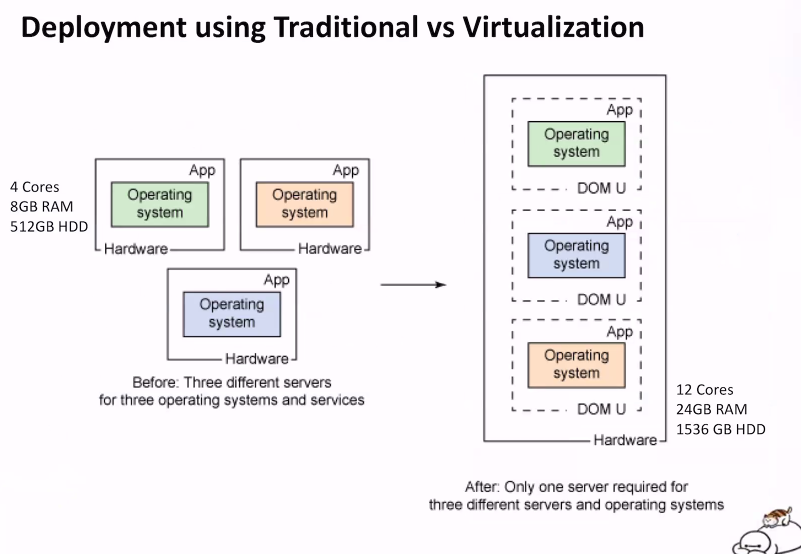
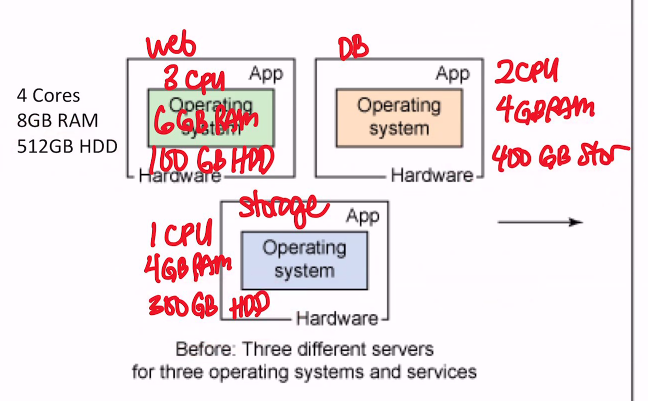
- youll need 700gb but the server is only 512gb
- combine all the needs in one server