STCLOUD_mod5_networking_content_delivery FULL
Announcements
- no long exam 2 this week
- long exam 2 will be on week 12
Module 5 Networking and Content Delivery
- this combines the notes from f2f
Networks
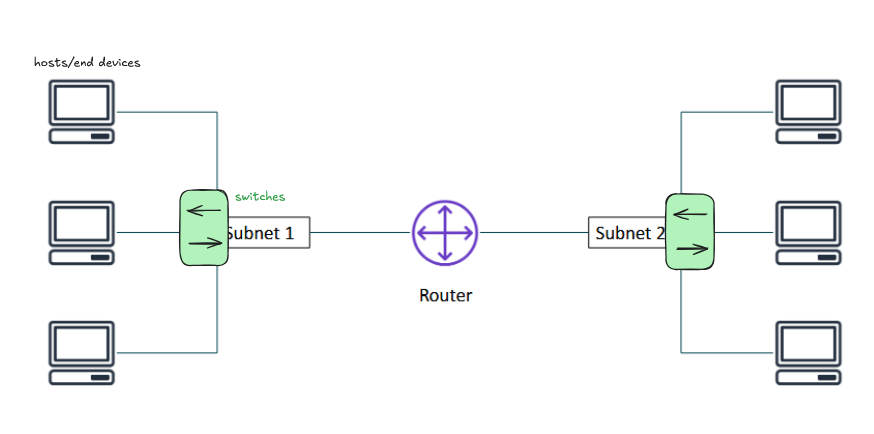
- public and private cloud, IaaS model (more flexibility if you're on this model) allows you to customize your network
- hosts for end-to-end connectivity
- intermediary devices: routers and switches
- there are capabilities to manipulate the networks when your setup is on the cloud
- knowing networking is important esp when you're dealing with an IaaS solution, which gives you access to lower level resources
end device/host A ← switch ← subnet 1 ← port A ← router → port B → subnet 2 → end device/host B
- routers route traffic between networks
- similar to intersections in a road
- our messages called packets go into the network and the router tells them where to go
- servers are end devices, your computers are end devices → the router allows end to end connectivity
IP Addresses
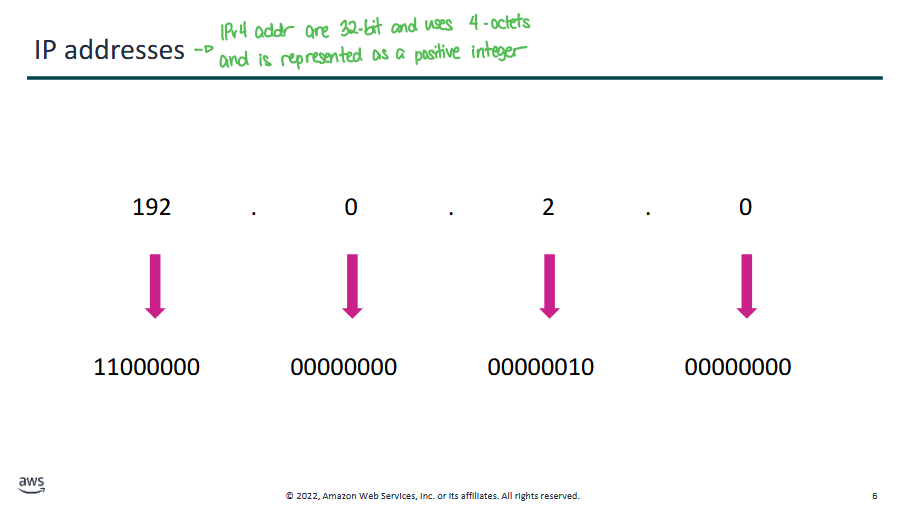
- IPv4 addresses are 32-bit and uses 4 octets, represented as a positive integer
- 2^32 (32 bit addr) = 4 bil addresses → 2^2 * 2^10 * 2^10 * 2^10
- 2^10 = 1024 or just ~1000
- 4 billion addresses is not enough for the entire world
there is an addressing scheme to identify hosts
- IP address is a unique identifier with a geological aspect, hence they are hierarchical in nature so it specifies areas in the world
- ranges from 0d to 255d for ipv4
IPv4 (32b) 192.0.2.0
IPv6 (128-bit) 2600:1f18:22ba:8c00:ba86:a05e:a5ba:00FF
- 2600 is a hextet (16 bit value for 1 segment)
- 4 nibbles = 1 hex 0 to F (?????)
- there's no special reason why i highlighted certain parts of the address above
- IPv6 addresses are 128-bit and uses 8 hextets (16-bit), represented as 4 nibbles or hexadecimal
- ipv6 uses hextet since each part is a 16bit value
- supports limitations of ipv4 by having a larger address space
- more address space can accommodate more devices
NAT Network Address Translation
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
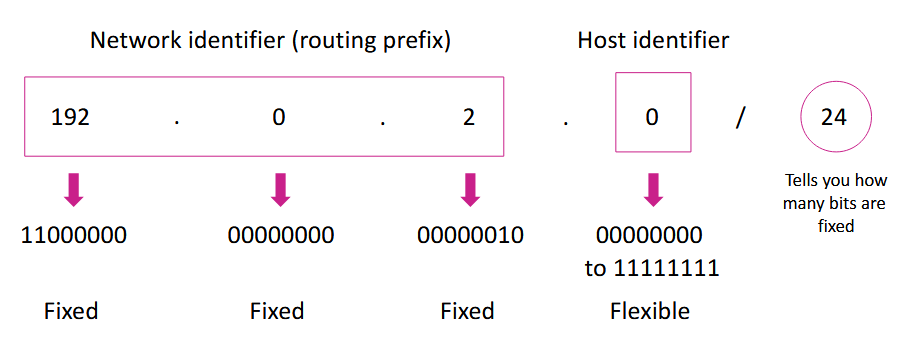
- IP addresses are used to identify YOUR specific device like a home address
- 192 = philippines, 0 = manila, 2 = taft avenue, .0 = lot number 2401 (for example lang, just to show that it's hierarchical and geographical)
- hierarchical in design to allow us to pinpoint where exactly in the world that specific device "is" ("is" because what if you're on a vpn lol)
- IP addresses have a separation (network portion, and host portion)
- think of the network portion as the subdivision
- the host portion as which house in the subdivision
- uses the subnet mask (255.255.255.0)
- the prefix length performs a bitwise AND operation from IP network and subnet mask to get the network address → to signify which bits are part of the network portion
- it is a set of 24 1s
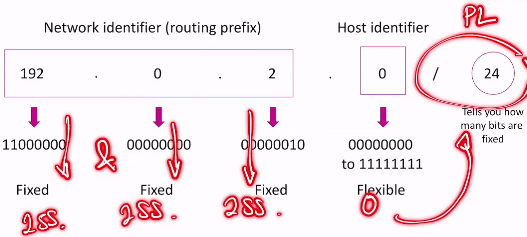
- the only thing written on the slide/summary: the subnet mask or prefix length (/24) is used to identify the Network and Host portions of an IP address
- the router uses this address to know where to forward packets of data
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model
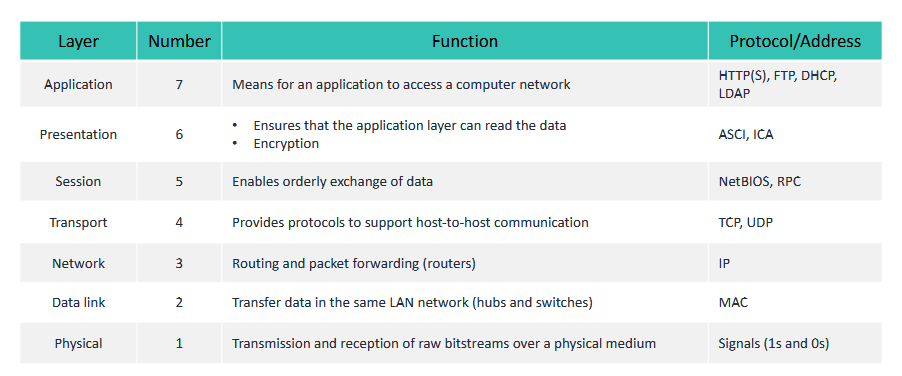
- OSI is a generic model for comms
- TCP/IP is the model we use for our computers
APP LAYER: application, presentation, session
TRANSPORT LAYER
NETWORK LAYER: internet
NETWORK ACCESS: data link, physical
Module 5 Section 2: Amazon VPC/Network Services
(24:59)
Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
- each account in the cloud is logically separated and isolated from other accounts
- in the cloud, each account is a tenant or a renter. you'll have your own environment that lets you customize things you want
- you can customize your particular instance without thinking about the other accounts
- you can make the necessary changes and adjustments to support the security requirements of your organization
- main point is you have control over customization
- enables you to provision a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud where you can launch AWS resources in a virtual network that you define
- gives you control over your virtual networking resources (for IaaS), including:
- selection of IP address range
- creation of subnets
- configuration of route tables and network gateways
- enables you to customize the network configuration (for IaaS) for your VPC
- enables you to use multiple layers of security
- network layer firewall + host base firewall + intrusion prevention system + logging server + MFA, etc.
Terminologies: VPCs and subnets
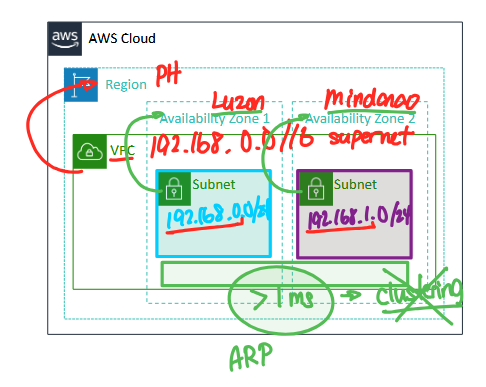
region first → VPC next → availability zone for the subnet
-
you can't create a subnet that encompasses 2 availability zones because of physical limitations (availability zones have different data centers, separate machines with separate configurations)
-
if you want clustering to happen there has to be >1ms latency
-
so you can't have the same network in 2 zones
-
VPCs
- logically isolated from other VPCs (your networks/supernets are logically isolated as well)
- ex. someone can have a supernet of 192.168.0.0 and another person's account can have the same address and that's fine because the instances are separated
- dedicated to your AWS account
- belong to a single AWS Region and can span multiple Availability Zones
- VPCs are like your super networks, your subnets will have to be subsets of the super net
- logically isolated from other VPCs (your networks/supernets are logically isolated as well)
-
Subnets/Network Segments
- range of IP addresses that divide a VPC
- belong to a single Availability Zone
- classified as public or private
Terminologies: IP Addressing
- VPC → Virtual Private Cloud/Network

- IP addressing
- you choose the size of your private network
- when you create a VPC, you cannot change the address range after you create the VPC
- IPv4 CIDR block sizes: /28 (smallest) to /16 (largest)
- those are the host bit lengths
- IPv6 is also supported with a different block size limit
- CIDR blocks of subnets cannot overlap
Prefix length PL is /16 or /28 represent the network bits
How to get the host bits?
- let's say we have 32 bits of IPv4
- subtract with the prefix length: 32bit - PL (/16) = 16 bits for host = 2^16 = 65k number of IP addresses that you can allocate in your network
- 32bit - /28 = 4 bits for host = 2^4 = 16 number of IP addresses that you can allocate in your network
you don't have to memorize how to get these addresses, that's for CSNETWK but you have to know that you HAVE flexibility in choosing these things
- if you chose a huge network but only have a few devices that's fine but you're paying for too much, once you used up all the IP addresses, you'll have to get another VPC
- if you got a small network but needed more IP addresses but you can't change it anymore
- so give it a bit of allowance → some addresses are reserved or unusable (all the addresses you get from /16 or /28, you have to subtract 5)
Reserved IP Addresses (5)
- you need to consider on allowance for reserved addresses when you decide on a block
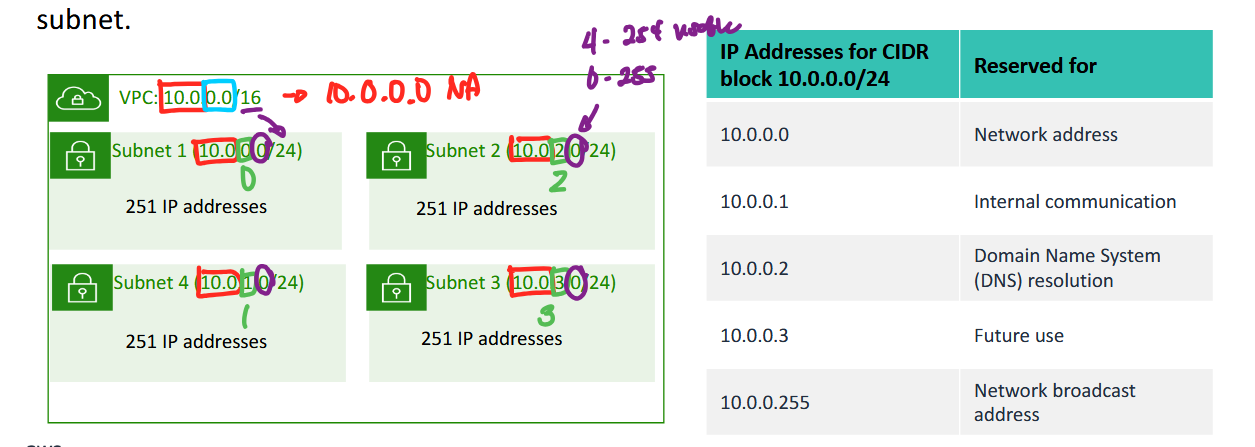
Example: a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR lock of 10.0.0.0/16 has 65,536 total IP Addresses. The VPC has 4 equal-sized subnets. Only 251 IP addresses are available for use by each subnet.
The reserved IP addresses:
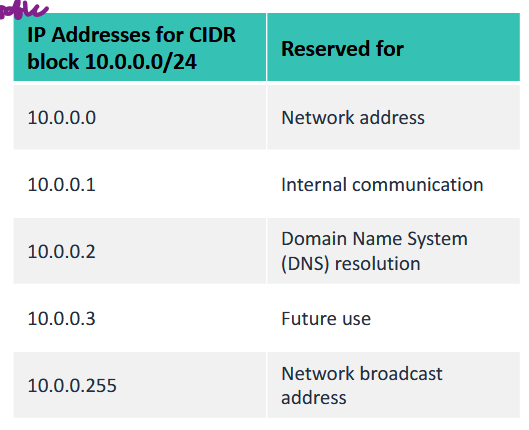
- traditionally, there are 2 unusable network addresses in a setup (one for Network Address and Network Broadcast Address)
- Network Address is the first IP address (used by routers to identify which path)
- Network Broadcast Address is the last IP address (for flooding or broadcasting addresses like THCP)
- The cloud provider will use an Internal Communication address (for the router)
- The cloud provider will also use a DNS Resolution address, and an extra Future Use address
if you chose a /28 prefix length
- 32bit - /28 = 4
- 2^4 = 16
- 16 - 5 = 11 usable addresses
- if you need 14 computers in your setup, you need another prefix length like /27
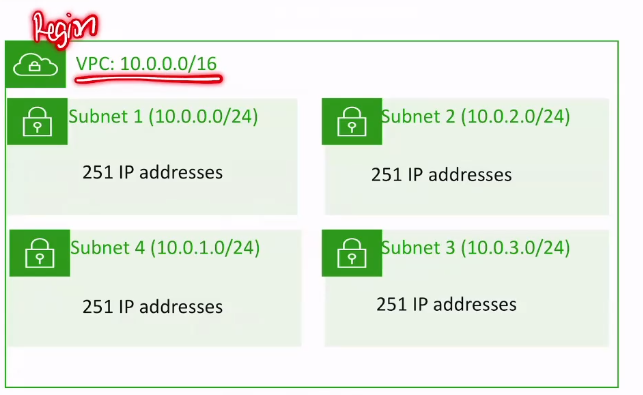
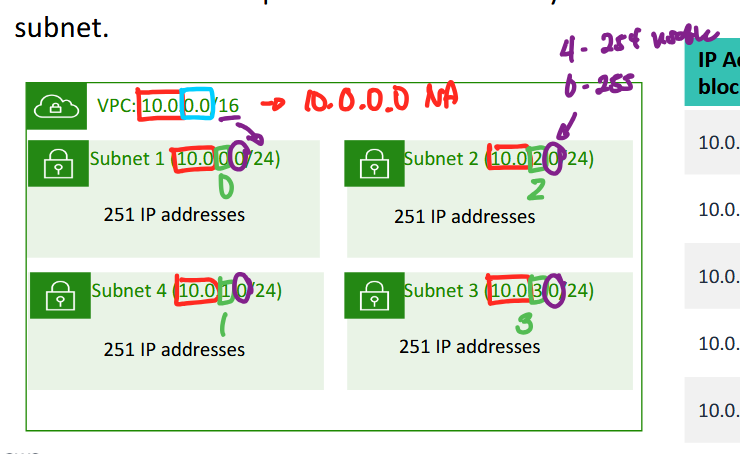
- this is a region with a corresponding VPC with network address 10.0.0.0
- (super) network portion: 10.0
- host portion: 0.0
- prefix length: /16
- then we have subnets with smaller portions /24 each
- the supernet portion is all 10.0 (RED)(matches the main network address)
- the next portion is 0 (GREEN) (which is the subnet identifier)
- the next portion is the host portion that ranges from 0-255 (PURPLE), with 4-254 actually usable addresses (remember that there are -5 reserved addresses)
- if you have more subnets it will consume more reserved IPs, with 5 to consume per subnet
Public IP address Types
public IP is important because we're dealing with public cloud → which needs internet access → reachable via the network
- Public IPv4 address
- temporary because it's assigned to the INSTANCE
- manually-assigned through an Elastic IP address
- automatically-assigned through the auto-assign public IP address settings at the subnet level
- address can change if you reboot your server or turn it off
- there's a "pool" of IP addresses
- public IP is temporary (bad thing if you're dealing with services, if you have a public website and service, your IP address can be allocated to someone else if you turn it off)
- people accessing your old DNS/your website can be given access to your OLD IP address
- use case: no public service, if you have some employees that need instances of VMs to use
- Elastic IP address
- associated with an AWS ACCOUNT (Elastic IP is the solution created by Amazon)
- can be allocated and remapped anytime
- additional costs might apply
- address is semi-permanent but you pay for a reservation cost if you use it or not
- use case: you manage a public service that people outside your organization to use
Route table and routes
57:17
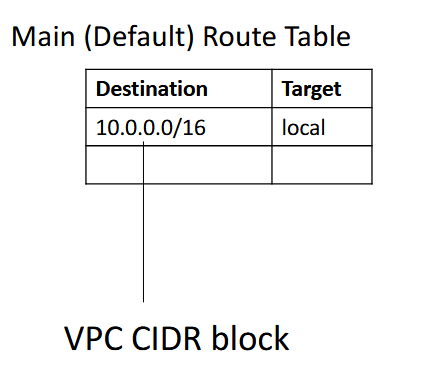
- used by the Network Services to route traffic between networks
- route table: contains a set of rules or routes that you can configure to direct network traffic from your subnet
- each route specifies a destination and a target
- by default: every route table contains a local route for communication within the VPC
- each subnet must be associated with a route table (at most one)
Module 5 Section 3: VPC Networking
58:06
Internet Gateway
don't have to memorize this, just appreciate how it works
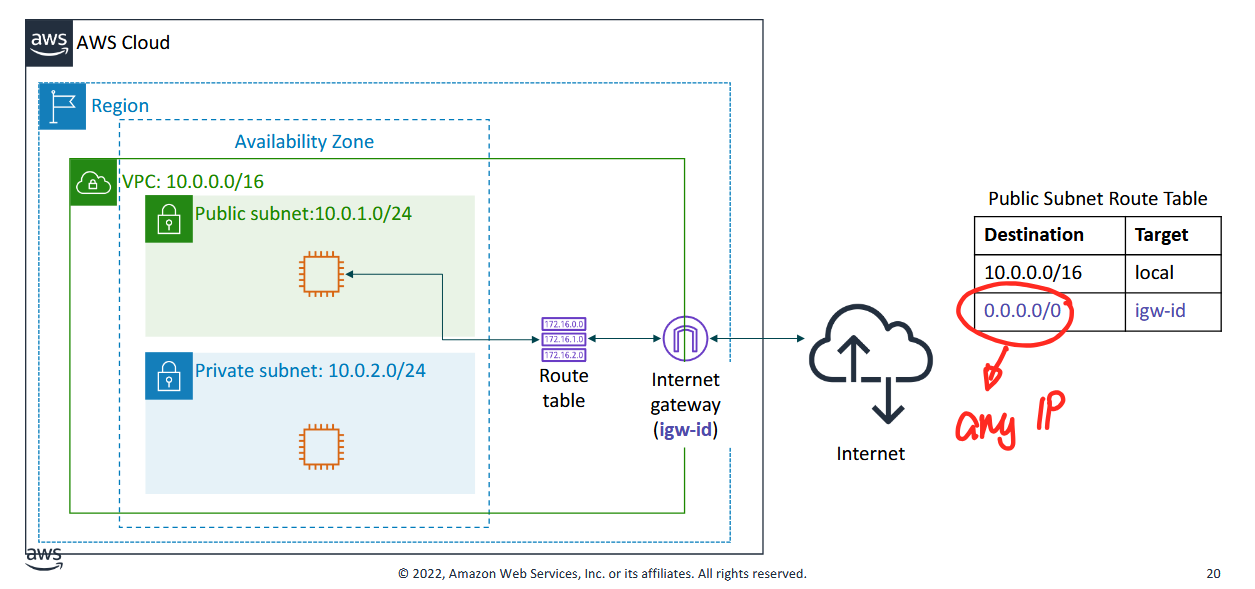
- the internet gateway allows us to connect to the internet
- it's for public subnets
- when you make a subnet, you define whether its private or public
- typically a private subnet wouldn't need an internet gateway but you'll need a NAT gateway for internet access
- it just adds an entry to the routing table
- 0.0.0.0/0* just means "any IP" is allowed
- "no match" = wildcard = any IP outside of the local network
- any IP besides local will be matched to the internet gateway
- there are wizards if you want a guide on making the networks
Network Address Translation (NAT) gateway
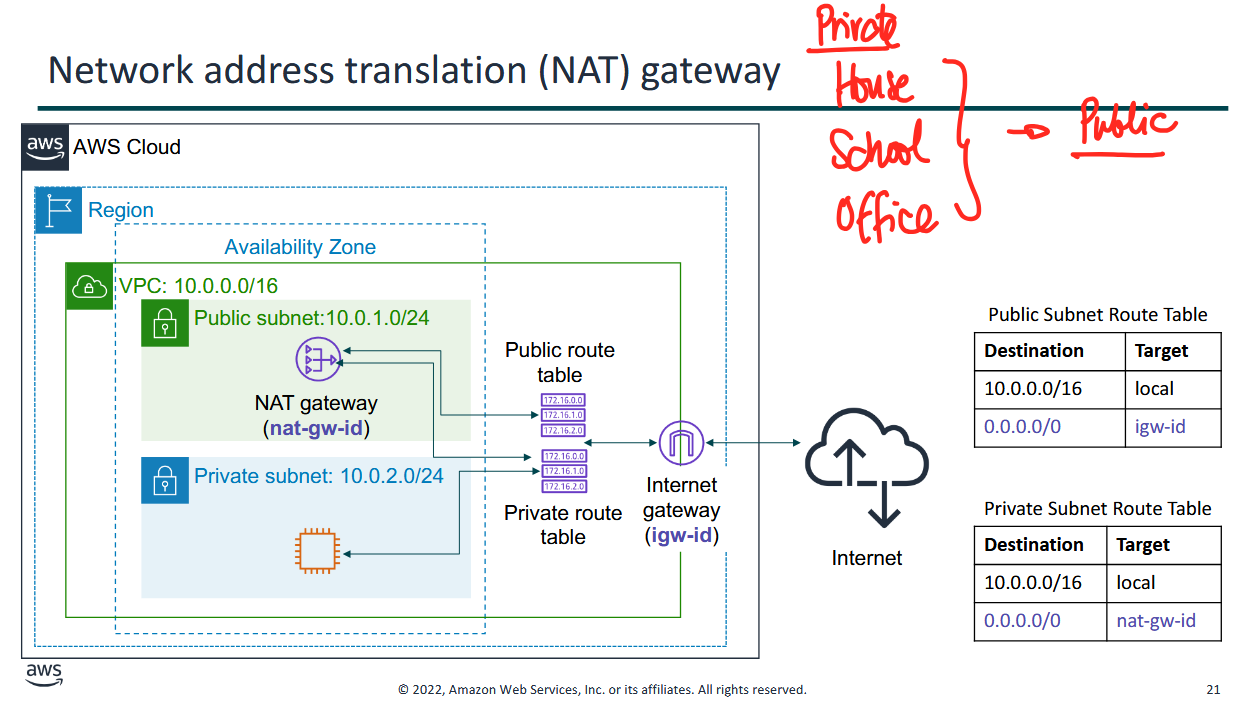
- NAT → used in our house, school, office
- translates an IP address from one side to another
- translates a private network into a public network
ipconfigwill show a private IP, public IP is on the router (one IP for the entire household for example)- awhile ago we had our Public Subnet Route Table, for example we had a private subnet that wanted to access the internet.
- if it's private, it's typically a local network
- if you have a PC A in the private subnet and you want it to connect to PC B in the public subnet, you match it to the local ip address and they will connect.
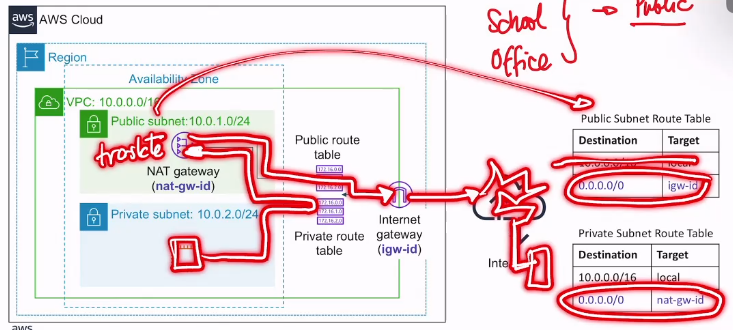
- if PC B wanted to connect to a server on the internet, PC B will send packets to the private route table, and it will go to the NAT gateway on the public subnet, perform NAT translation, then it will use the Public Subnet Route Table and go to the internet gateway
- private houses will use a NAT gateway to go to the internet, public networks will just go straight to the internet gateway
Section 4 VPC Security
1:06:48
- networks are just a series of conditions
- if networks give us access to different devices in the network, we have to look at security to protect your data and your servers
- there are 2 major ways to secure our data in the network
- security groups (host-based firewalls)
Security Groups
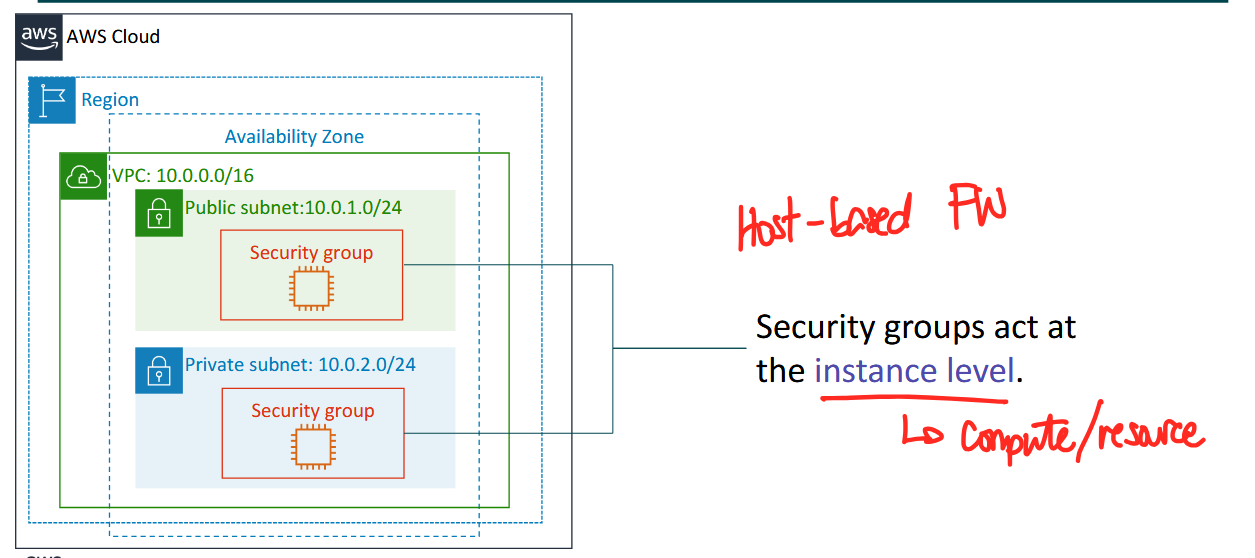
- security groups are host-based firewalls
- they act at the instance level → compute/resource
- before a packet goes into the public subnet, it will be evaluated by the security group first before being allowed through or not
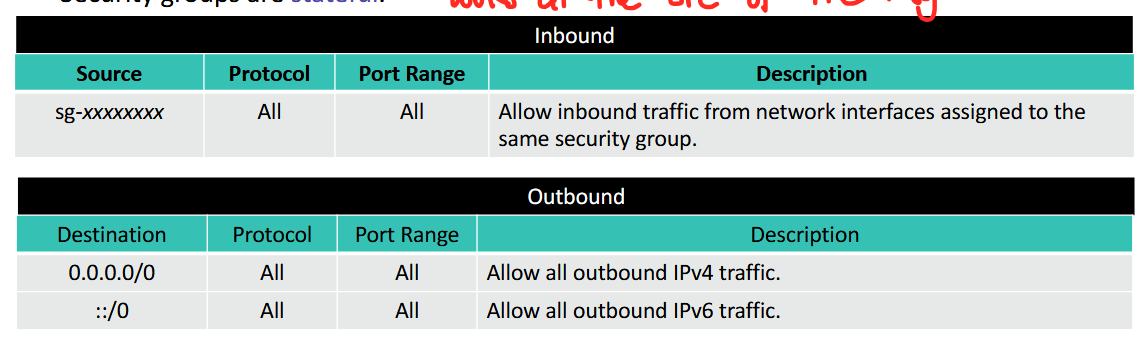
- security groups have rules that control inbound and outbound instance traffic
- rules are like if statements
- default security groups: deny all inbound traffic (origin comes from outside) and allow all outbound traffic
- by default you're following a good security practice of no access from other entities
- security groups are stateful → looks at the source of the message
- because it's stateful, all traffic coming FROM your machine can come back to your machine (if the source came from you and your machine gives a reply it will come back to you)
- bale it's just allowing stuff from you
- if you need to deploy a web server, you create a configuration/rules to allow that
Custom Security Group Examples
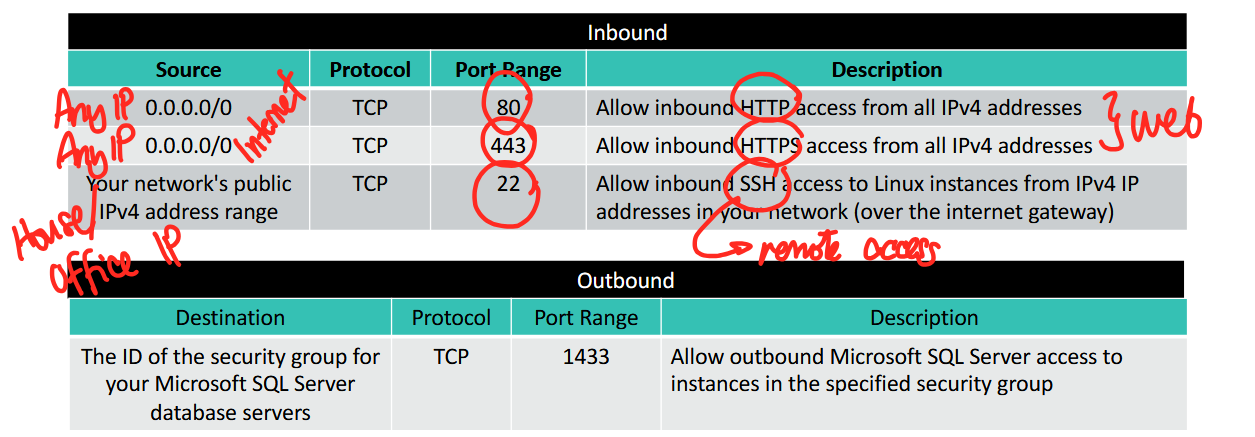
- you can specify allow rules, but not deny rules
- it's already deny by default eh
- all rules are evaluated before the decision to allow traffic (think huge if-statements)
Inbound Rules
- source 0.0.0.0/0 (any IP or wildcard) → anyone in the world can communicate with your server
- TCP → connection-oriented and reliable, for transferring data like HTML files, CSS files, images
- port 80 → HTTP (web access)
- post 443 → HTTPS (web access)
first 2 inbound rules
- allows web access
3rd inbound rule - your networks public IP range → able to communicate via SSH (remote access, Secure Shell) allow only your house or office to remote access your VM
Network Access Control Lists (Network ACLs)
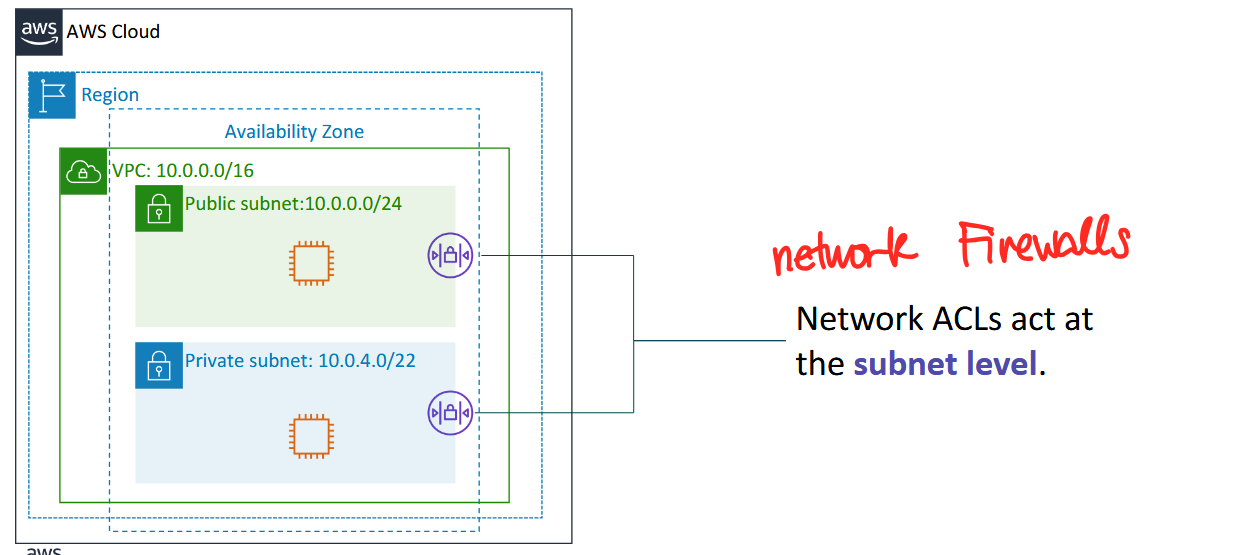
- network ACLs are network firewalls that act at the subnet/network level
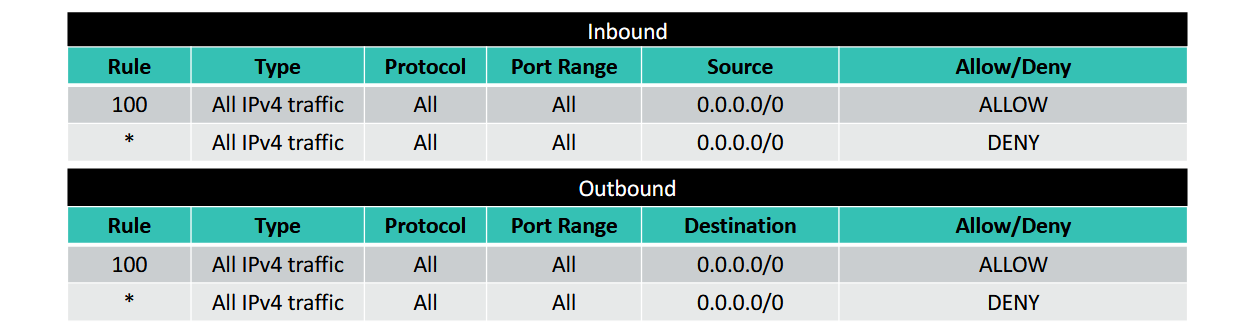
- a network ACL has separate inbound and outbound rules, and each rule either allow or deny traffic
- default is allow (while security group is deny by default)
- default: allow all inbound and outbound IPv4 traffic
- network ACLs are stateless → they do not look at the origin of the traffic
- rule numbers: ordering
Custom Network ACL Example
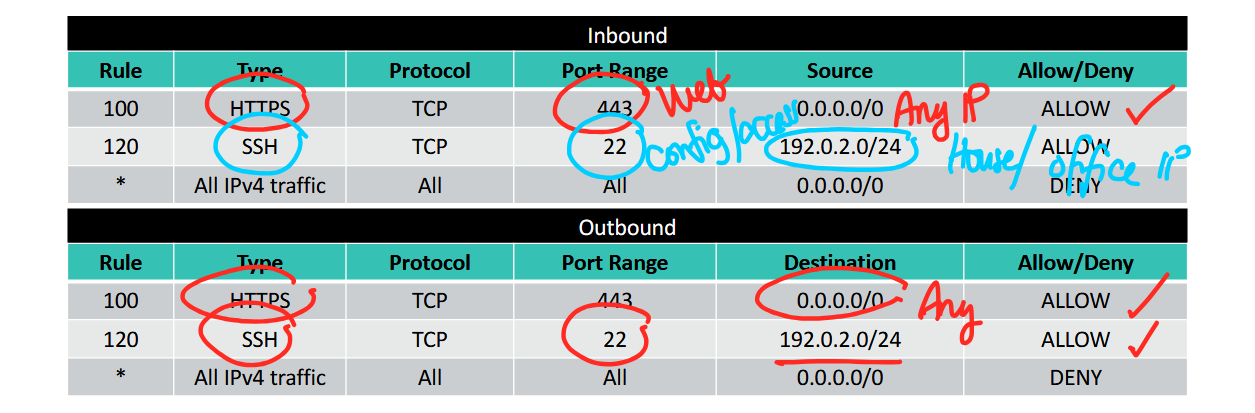
- custom network ACLs deny all inbound and outbound traffic until you add rules
- you can specify both allow and deny rules
- rules are evaluated in number order, starting with the lowest number
1st rule: Rule # 100 → HTTPS → port 443 web traffic from any IP → ALLOW
- anyone from the internet is allowed to send web traffic
2nd rule: Rule # 120 → SSH → port 22 → 192.0.2.0/24 → ALLOW - port 22 means remote config/access
- includes specific IP (house/office IP)
- if the traffic comes from said IP, allow SSH traffic
for the 1st and 2nd rule in Inbound, you need a complementary outbound rule that does the same thing so in/out traffic will be allowed
3rd rule: Rule * → all IPv4 traffic → all ports and protocols → 0.0.0.0/0 (wildcard) → DENY
- bale anyone else trying to access is blocked
put descriptions and labels on your rules so you can understand and remember what they do, convert them to english
Summary: Security Groups vs Network ACLS
1:20:20
| Attribute | Security Groups | Network ACLs |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Instance-level (Host-based Firewall) | Subnet level (Network Firewall) |
| Supported Rules | Allow rules only, deny by default | Allow and deny rules |
| State | Stateful (return traffic (from you) is automatically allowed, regardless of rules) | Stateless (return traffic must be explicitly allowed by rules) |
| Order of rules | all rules are evaluated before decision to allow traffic | rules are evaluated in number order before decision to allow traffic, lowest number first |
Module 5 Section 5: Amazon Route 53 (DNS)
1:25:03
Amazon Route 53 (DNS Service)

- DNS: Domain Name System → converts a name to an address
- 53 is the port number of DNS
- a highly available and scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service
- used to route end users to interpret applications by translating names (like www.google.com) into numeric IP addresses (192.0.2.1) that computers use to connect to each other
- is fully compliant with IPv4 and IPv6
- connects user requests to infrastructure running in AWS and also outside of AWS
- used to check the health of your resources
- features traffic flow
- enables you to register domain names
Amazon Route 53 supported Routing
- Simple routing - use in single-server environments
- if you want to go to dlsu.edu.ph it will always give you one IP address
- i have a name, give me an IP
- Weighted round robin routing - assign weights to resource record sets to specify the frequency (multi-server)
- what if you have many servers around the world running the same service
- weighted → prioritizes one server more than the others
- Latency routing - help improve your global applications
- when you request for an IP address, it also looks at your latency between you and the application, then it gives you the lowest latency IP address
- Geolocation routing - route traffic based on location of your users
- if it recognizes you're in the philippines via ur IP, it will bring you to domain.com.ph
- if it recognizes you're in the philippines via ur IP, it shows you relevant philippine content
- Geoproximity routing - route traffic based on location of your resources
- the same thing but for resources (caches, servers)
- Failover routing - fail over to a backup site if your primary site becomes unreachable
- (1:28:00) let's say you have a multi-server setup but you don't want the multiple servers to run. idk what sir is talking about here
- if your current website is currently undergoing maintenance, the IP address will reroute to a backup server with less resources
- Multivalue answer routing - respond to DNS queries with up to eight healthy records selected at random
- (1:30:38) if you have a DNS query and you have many many servers, it can give you multiple records at a time. so the requesting PC can access all the other IPs at a time in case some aren't working
recording ended here
Use Case: Multi-region Deployment
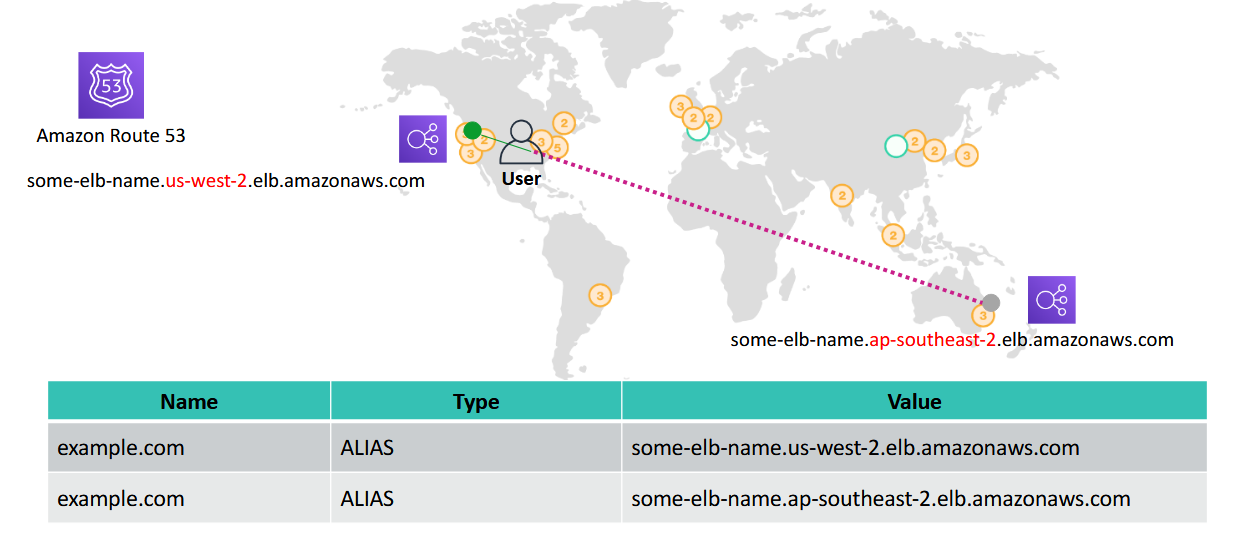
Amazon Route 53 DNS failover
- improve the availability of your applications that run on AWS by
- configuring backup and failover scenarios for your own applications
- enabling highly available multi-region architectures on AWS
- creating health checks
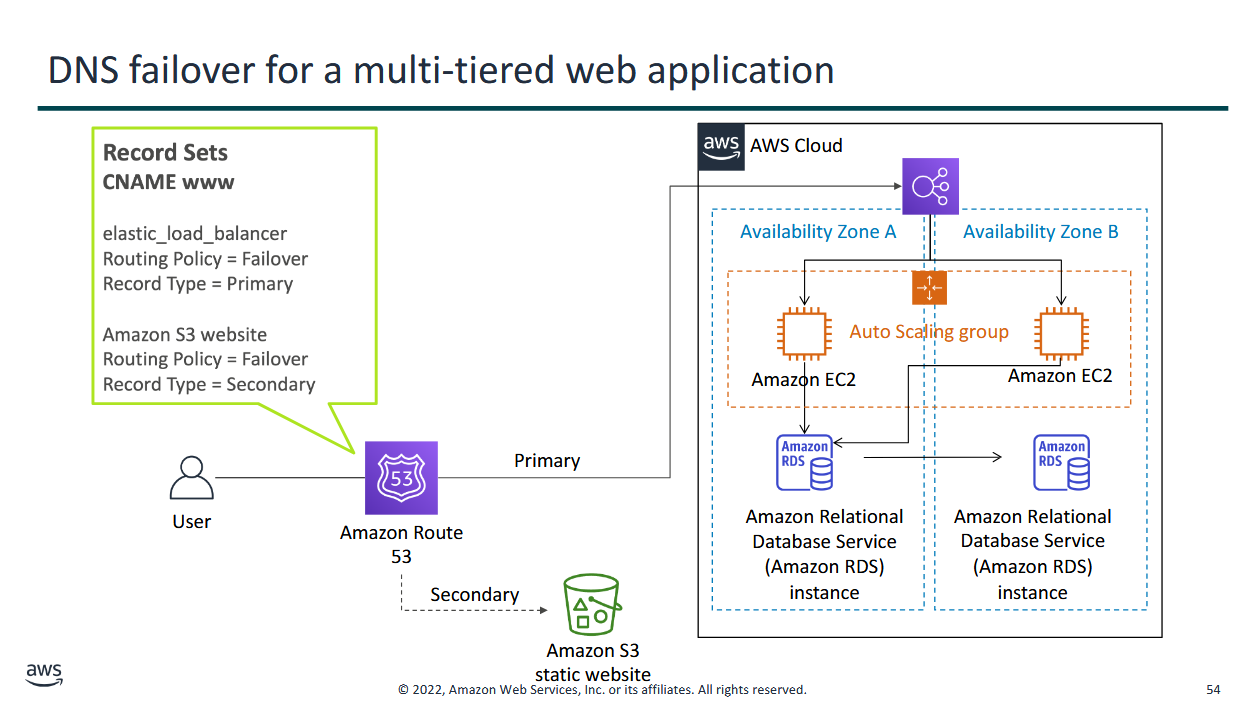
DNS failover for a multi-tiered web application
Module 5 Section 6 Amazon CloudFront
Content Delivery and Network Latency
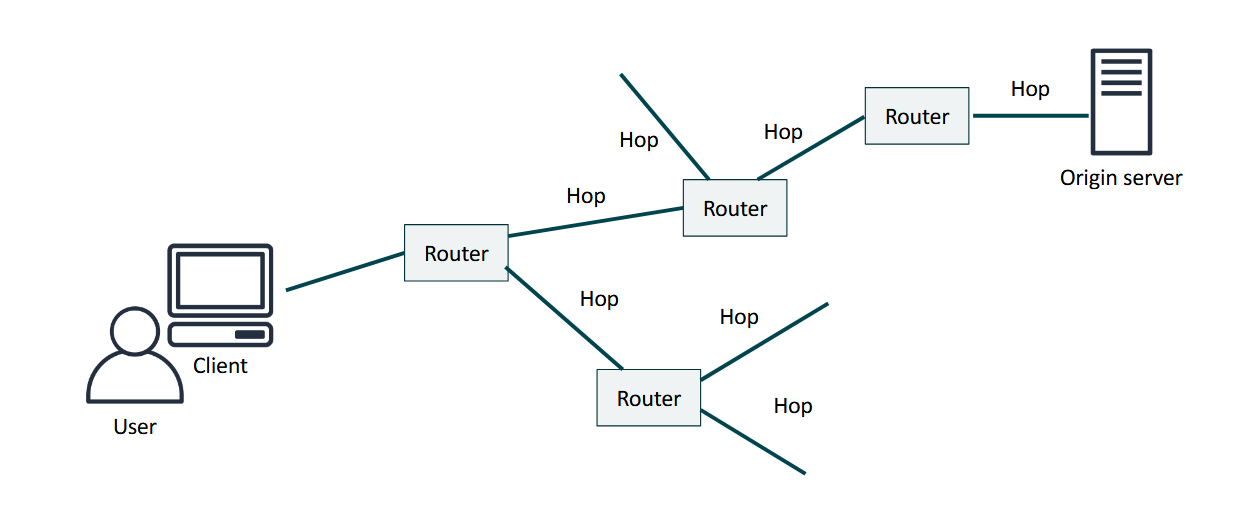
- you have to go thru multiple routers in order to reach the origin server and vice versa
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- globally distributed system of caching servers
- caches copies of commonly requested files (static content like images, pages, etc.)
- delivers a local copy of the requested content from a nearby cache edge or Point of Presence
- accelerates delivery of dynamic content
- improves application performance and scaling
Amazon CloudFront Infrastructure
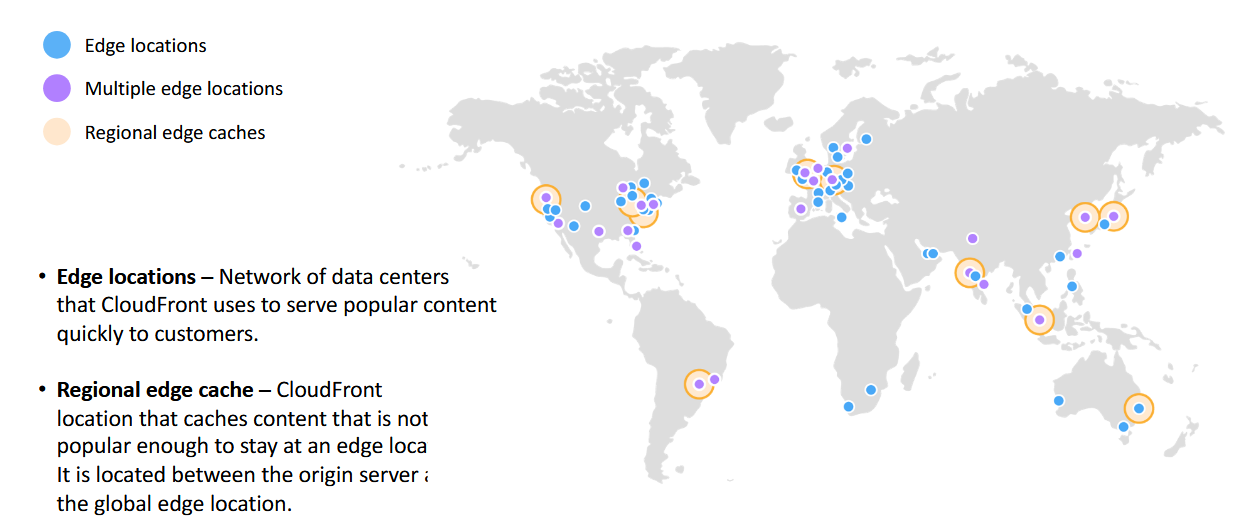
- edge locations: network of data centers that CloudFront uses to serve popular content quickly to customers
- regional edge cache: CloudFront location that caches content that is not popular enough to stay at an edge location
- is located between the origin server and the global edge location
Amazon CloudFront benefits
- fast and global
- security at the edge
- highly programmable
- deeply integrated with AWS
- cost-effective