STCLOUD_mod8_databases FULL
original file
last module, 39:13
Module 8 Databases
Types of Databases
- Relational/SQL DB
- Non-relational/No-SQL
- Data Warehousing (Big data analytics)
- Enterprise SQL
- Manual DB (get a VM and install an SQL engine)
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS)

- SQL-based
Unmanaged vs Managed Services
| Unmanaged | Managed |
|---|---|
| Scaling, fault tolerance, and availability are managed by you | Scaling, fault tolerance, and availability are built into the service/handled by the provider |
| higher flexibility and configurability, more responsibility but also more contorl | less responsibility, you focus on your data |
| cheaper | pricier |
| when you're using a VM | when you're using the DB services |
Challenges of Relational Databases
things you have to think about in the traditional/unmanaged sense
- server maintenance and energy footprint
- software installation and patches
- database backups and high availability
- limits on scalability
- data security
- operating system (OS) installation and patches
if you know how to do these and you can do them yourself it's gonna be cheaper
Amazon RDS
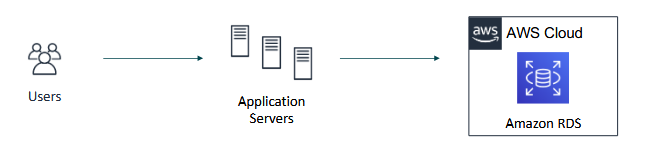
- a managed service that sets up and operates a relational database in the cloud
From on-premises databases to Amazon RDS
bold → managed by AWS
| On-premises DB (traditional) -> | DB in Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) (cloud VM + db engine) -> | DB in Amazon RDS or Aurora (db service) |
|---|---|---|
| application optimization | application optimization | application optimization |
| scaling | scaling | scaling |
| high availability | high availability | high availability |
| database backups | database backups | database backups |
| database software patches | database software patches | database software patches |
| database software installs | database software installs | database software installs |
| operation system patches | operation system patches | operation system patches |
| operating system install | operating system install | operating system install |
| server maintenance | server maintenance | server maintenance |
| rack and stack servers | rack and stack servers | rack and stack servers |
| power, HVAC, network | power, HVAC, network | power, HVAC, network |
- traditional → you do everything
- Cloud VM + DB engine → they take care of physical (OS above is your responsibility)
- DB services → they take care of a lot of things and then you focus on your application optimization nalang
Managed Services Responsibilities
- YOU: application optimization
- AWS:
- OS installation and patches
- database software installation and patches
- database backups
- high availability
- scaling
- power and racking and stacking servers
- server maintenance
Amazon RDS DB Instances
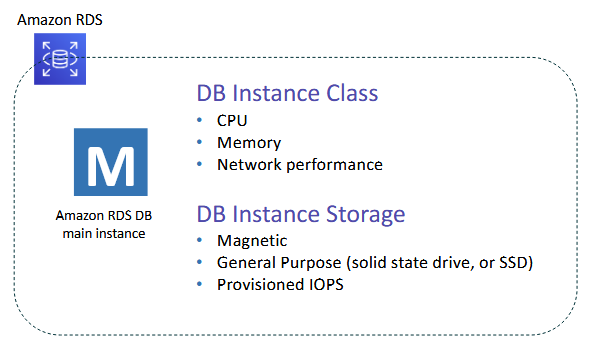
- columns and tables with foreign keys connecting one thing to another
- MySQL, Amazon Aurora, Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle
- DB engines
Amazon RDS in a VPC (virtual private cloud)
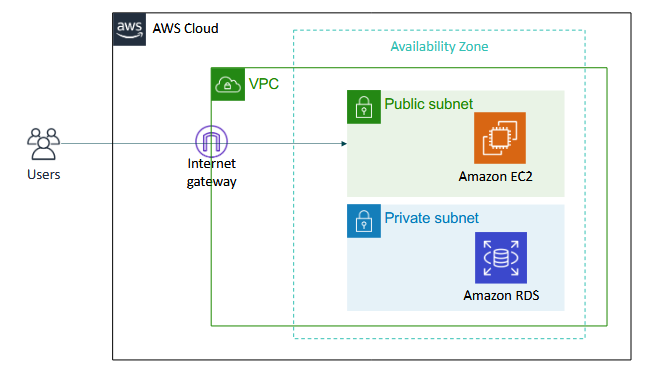
- put the database in a private subnet for security
- users from outside can access the VM
High Availability with Multi-AZ deployment
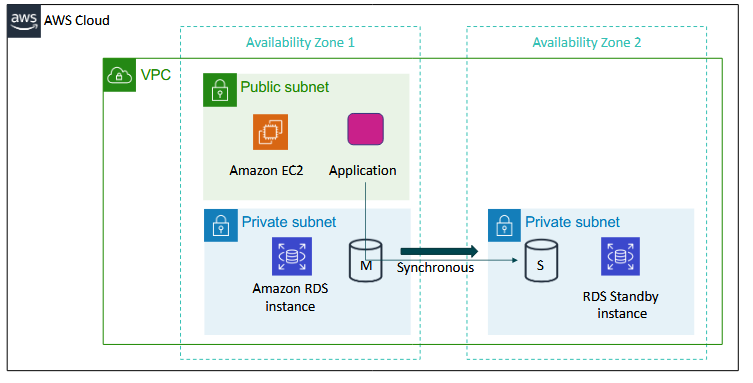
- VM and application are on the public subnet
- master and slave setup (master copies to slave) for backups
- so when the master isn't working, it will connect to the slave backup and the slave will be promoted to master
there are many architectural advantages you can setup in the cloud to ensure the data will not be lost
Amazon RDS Read Replicas
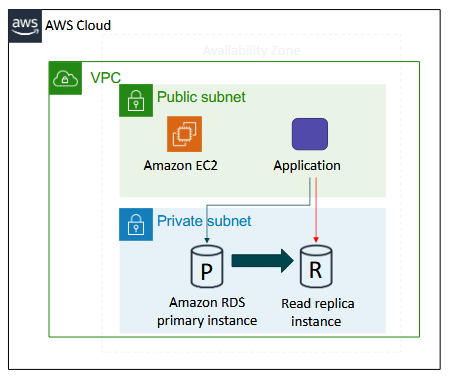
Read from a replica when there's high amount of load/traffic on one
Load balancing of transactions
Features
- offers asynchronous replication
- can be promoted to primary if needed
Functionality - use for read-heavy database workloads
- offload read queries
Use Cases
| Web and Mobile Applications | - high throughput - massive storage scalability - high availability |
|---|---|
| Ecommerce applications | - low cost database - data security - fully managed solution |
| Mobile and online games | - rapidly grow capacity - automatic scaling - database monitoring |
When to use Amazon RDS
Use when your application requires...
- complex transactions or complex queries
- a medium to high query to write rate - up to 30,000 IOPS (15k reads + 15k writes)
- no more than a single worker node or shard
- high durability
Do not use when your application requires. - massive read/write rates (150k write/sec) → use Enterprise SQL
- sharding due to high data size or throughput demands → use Data Warehousing
- simple GET or PUT requests and queries that a NoSQL database can handle → use a Non Relational DB
- relational database management system (RBDMS) customization → get a VM and install your DB engine
Module 8 Section 2: Amazon DynamoDB
Relational vs Non-relational
- non-SQL/non-relational: JSON, XML, etc. (horizontal scaling)
- while SQL/relational: fixed columns (vertical scaling - many entries, same column length)
| Relational (SQL) | Non-Relational | |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | rows and columns | key-value, document, graph |
| Schemas | fixed | dynamic, flexible |
| Querying | uses SQL | focuses on collection of documents/data |
| example | 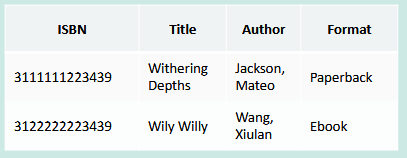 |
 |
| all the columns have fixed amounts or have a strict formatting | it's possible that some might not have an author or format (difference in varying cols) |
What is Amazon DynamoDB

- fast and flexible NoSQL database service for any scale
- noSQL database tables
- virtually unlimited storage
- items can have differing attributes
- low-latency queries
- scalable read/write throughput
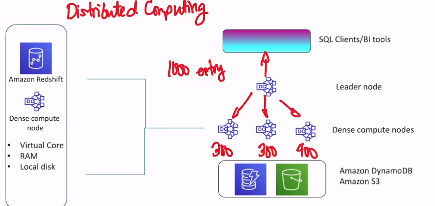
Amazon Redshift
- for data warehousing → for analytics, business intelligence
Parallel Processing Architecture
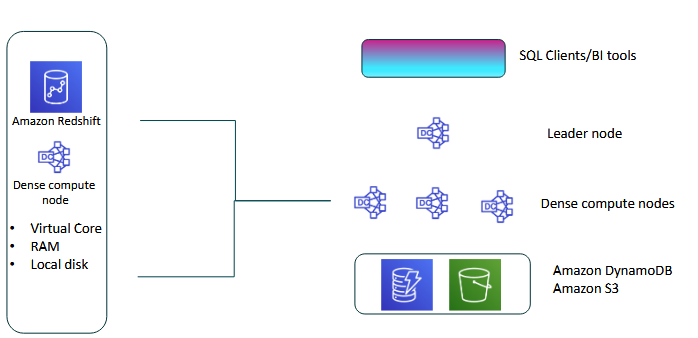
- kind of like distributed computing
- the leader node can distribute load to other nodes to perform
What can it do
- automation and scaling
- manage, monitor, scale
- compatibility
- Amazon Redshift 🤝 SQL Clients & business intelligence (BI) tools
Amazon Redshift use cases
- Enterprise data warehouse (EDW)
- migrate at a pace that customers are comfortable with
- experiment without large upfront cost or commitment
- respond faster to business needs
- Big Data
- low price point for small customers
- managed service for ease of deployment and maintenance
- focus more on data and less on database management
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- scale the data warehouse capacity as demand grows
- add analytic functionality to applications
- reduce hardware and software costs
Amazon Aurora (Enterprise RDB/SQL)
1:00:34

- enterprise-class relational database
- compatible with MySQL or PostgreSQL
- automate time-consuming tasks (like provisioning, patching, backup, recovery, failure detection, repair)
- Aurora itself is the engine, this is SaaS (the rest kanina are PaaS)
Amazon Aurora Service Benefits
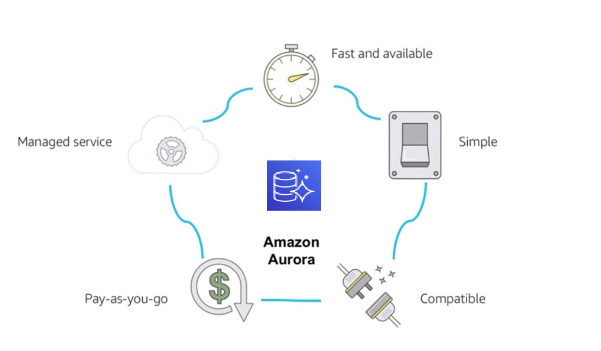
- managed
- pay-as-you-go
- fast and available
- simple
- compatible
- high availability
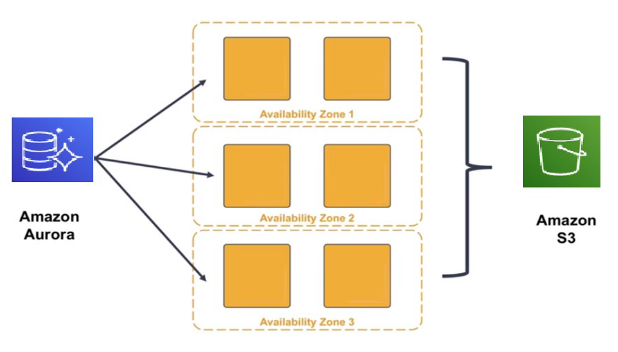
- resilient design
Summary: The right tool for the right job
| what are your requirements? | |
|---|---|
| enterprise-class relational database | Amazon RDS, SQL or Enterprise SQL |
| Fast and flexible NoSQL database service for any scale | Amazon DynamoDB, noSQL DB |
| Operating system access or application features that are not supported by AWS database services | Databases on Amazon EC2 (VM + DB engine) |
| Specific case-driver requirements (machine learning, data warehouse, graphs) | AWS purpose-built database services (other) |